韦伦斯症候群
| 韦伦斯症候群 Wellens' syndrome | |
|---|---|
| 同义词 | 韦伦斯征象(Wellens' sign)、Wellens' warning、韦伦斯波(Wellens' waves) |
 | |
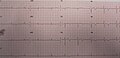
| 一名69岁黑人男性患者的心电图。图中可以看到V1-V4导极双相型T波,且由正转负。 | |
| 分类和外部资源 | |
| 医学专科 | 心脏内科 |
| eMedicine | 1512230 |
韦伦斯症候群(Wellens' syndrome),是左前降支动脉(left anterior descending,LAD)狭窄型的不稳定性心绞痛所特有的心电图变化[1]。该征象对诊断左前降支狭窄具有高度特异性[2]。
描述[编辑]
典型心电图变化为胸前导极(V2、V3)出现双极性T波或T波倒置的情形。该征象最初被分为A、B两型,但后来认为是同一种症候群在不同时间点的时序性变化。一开始会呈现对称的双相型(biphasic)T波倒置,后来会逐渐在胸前导极形成倒深T波[1]。
Rhinehart等人在2002年对该症候群进行下列描述[3]:
- V2、V3双极性T波或倒深T波(可能延伸至V1-6)
- ST段微幅(< 1mm)或没有升高
- 胸前导极无Q波出现
- R波递增(R wave progression)正常
- 近期有心绞痛病史
- 该心电图变化通常发生于无痛期(pain-free state)
- 心脏酵素正常或微幅上升
临床意义[编辑]
该征象在诊断及预后评估上具有重要的价值。有研究发现,该症候群所有患者的左前降支动脉皆阻塞面积超过50%,平均阻塞面积则高达85%[4]。在诊断左前降支动脉(LAD)狭窄的敏感度为24.6%,特异度为96.2%,具有高度特异性,意即发生此征象者有极高的机会具有左前降支狭窄的问题[2][5]。
有病例报告显示压力性心肌症(Takotsubo cardiomyopathy)也会有此变化[6]。
治疗[编辑]
若缺乏治疗,患者的病程极可能会进展至心肌梗塞。因此除抗血栓药物治疗之外,若无禁忌症,建议进行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)进行根本治疗[2]。
流行病学[编辑]
韦伦斯症候群并非罕见状况,约有14%-18%的不稳定性心绞痛入院的患者会如此表现[7],且约8.8%患者具有非ST上升型心肌梗塞(NSTEMI)的情形。若在初次发病后,持续监测心电图24小时,则高达六成的患者在某段时间会有此表现。
发现[编辑]
1979年,葛森(Gerson)等人描述了一群近端LAD狭窄的患者,在进行活动时,胸前导极的心电图出现了“U波”,当时所指的“U波”是指双相性T波后半段倒置的部分[8]。1982年,亨里克·琼·乔斯特·韦伦斯(Hein J. J. Wellens)等人根据一群不稳定性心绞痛患者描述了此征象[9]。
图像[编辑]
-
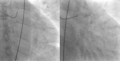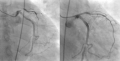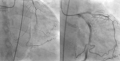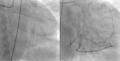
动态冠状动脉照影术。左图显见患者近端LAD严重狭窄(95%),右图为通血管之后的影像,可以完整看到LAD。
-
胸痛期的心电图,图中V2-V3并无倒置。
-
无痛期的心电图,可以看到V2-V3呈现双极性T波。
参考文献[编辑]
- ^ 1.0 1.1 Tandy, TK; Bottomy DP; Lewis JG. Wellens' syndrome. Annals of Emergency Medicine. March 1999, 33 (3): 347–351 [2021-03-19]. PMID 10036351. doi:10.1016/S0196-0644(99)70373-2. (原始内容存档于2020-01-13). 引用错误:带有name属性“:0”的
<ref>标签用不同内容定义了多次 - ^ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Miner, Brianna; Grigg, William S.; Hart, Elise H. Wellens Syndrome. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021 [2021-03-19]. PMID 29494097. (原始内容存档于2021-02-27).
- ^ Rhinehardt, Joseph; Brady, William J.; Perron, Andrew D.; Mattu, Amal. Electrocardiographic manifestations of Wellens' syndrome. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2002-11, 20 (7): 638–643 [2021-03-19]. ISSN 0735-6757. PMID 12442245. doi:10.1053/ajem.2002.34800. (原始内容存档于2022-01-21).
- ^ Haines, D. E.; Raabe, D. S.; Gundel, W. D.; Wackers, F. J. Anatomic and prognostic significance of new T-wave inversion in unstable angina. The American Journal of Cardiology. 1983-07, 52 (1): 14–18 [2021-03-19]. ISSN 0002-9149. PMID 6602539. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(83)90061-9. (原始内容存档于2022-04-24).
- ^ Kobayashi, Akihiro; Misumida, Naoki; Aoi, Shunsuke; Kanei, Yumiko. Prevalence and Clinical Implication of Wellens’ Sign in Patients With Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Cardiology Research. 2019-6, 10 (3): 135–141. ISSN 1923-2829. PMC 6575113
 . PMID 31236175. doi:10.14740/cr856.
. PMID 31236175. doi:10.14740/cr856.
- ^ Taylor, R. Scott; Skjerli, Leif; Ashurst, John. Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Presenting as Wellens’ Syndrome. Clinical Practice and Cases in Emergency Medicine. 2017-05-24, 1 (3): 175–178. ISSN 2474-252X. PMC 5965163
 . PMID 29849266. doi:10.5811/cpcem.2017.1.32297.
. PMID 29849266. doi:10.5811/cpcem.2017.1.32297.
- ^ de Zwaan, C; Bär FW; Janssen JH; et al. Angiographic and clinical characteristics of patients with unstable angina showing an ECG pattern indicating critical narrowing of the proximal LAD coronary artery. American Heart Journal. March 1989, 117 (3): 657–665. PMID 2784024. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(89)90742-4.
- ^ Gerson, M. C.; Phillips, J. F.; Morris, S. N.; McHenry, P. L. Exercise-induced U-wave inversion as a marker of stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Circulation. 1979-11, 60 (5): 1014–1020 [2021-03-19]. ISSN 0009-7322. PMID 487534. doi:10.1161/01.cir.60.5.1014. (原始内容存档于2022-06-15).
- ^ de Zwaan, C; Bär FW; Wellens HJJ. Characteristic electrocardiographic pattern indicating a critical stenosis high in left anterior descending coronary artery in patients admitted because of impending myocardial infarction. American Heart Journal. April 1982, 103 (4): 730–736. PMID 6121481. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(82)90480-X.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||