羟胺-O-磺酸
| 羟胺-O-磺酸 | |
|---|---|

| |

| |
| 英文名 | Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid |
| 识别 | |
| CAS号 | 2950-43-8 |
| PubChem | 76284 |
| ChemSpider | 68763 |
| SMILES |
|
| EINECS | 220-971-6 |
| 性质 | |
| 化学式 | H3NO4S |
| 摩尔质量 | 113.09 g·mol−1 |
| 外观 | 白色至米色固体[1] |
| 密度 | 2.2 g/cm3[2] |
| 熔点 | 210 °C(分解)[1] |
| 溶解性(水) | 675 g/L,缓慢分解[2] |
| 溶解性 | 可溶于甲醇和DMSO[3] 不溶于非极性溶剂[3] |
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |
羟胺-O-磺酸是化学式 H3NO4S的无机化合物,可以由羟胺和发烟硫酸反应而成。[4]它是白色、可溶于水、易潮解的固体,以两性离子+H3NOSO3−存在。[5]它被用作胺化试剂,也用于把醛转化成腈,把环酮转化成内酰胺,以及各种含氮杂环的合成。[5][6][7]
制备
[编辑]实验室的羟胺-O-磺酸是由羟胺和发烟硫酸的反应制备的,[4]而工业生产羟胺-O-磺酸的生产过程也是这样。[8]
- (NH3OH)2SO4 + 2SO3 → 2H2NOSO3H + H2SO4
结构
[编辑]类似氨基磺酸(H3N+SO3−)和氨基酸,羟胺-O-磺酸在固态下以两性离子 H3N+OSO3−的形式存在。[9]
反应
[编辑]羟胺-O-磺酸在碱性环境下是亲核体,在酸性条件下是亲电体。[6][10]

胺化反应
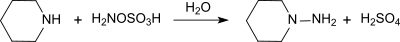
[编辑]羟胺-O-磺酸和伯胺、仲胺反应会分别产生对应的肼。举个例子,它和哌啶反应,生成N-氨基哌啶,产率96%。[11]

苯并三唑被羟胺-O-磺酸N-胺化,产生1-氨基苯并三唑(主产物)和2-氨基苯并三唑。1-氨基苯并三唑被乙酸铅(IV)氧化会产生苯炔,然后迅速二聚成联苯烯。[13]

像是四唑的缺电子杂环化合物可以被羟胺-O-磺酸N-胺化,而更缺电子的5-硝基四唑则只能和更强的胺化试剂(如O-对甲苯磺酰基羟胺)反应。[14]

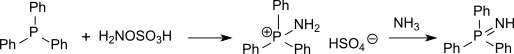
硫醚可以被羟胺-O-磺酸胺化成亚氨基硫醚(结构和亚砜相似但很不稳定),而膦则会被胺化成亚氨基膦。[15]

羟胺-O-磺酸和亚磺酸盐在乙酸钠溶液中反应可以得到磺酰胺,产率很高。[16]
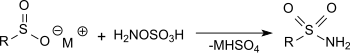
和羰基化合物的反应
[编辑]在室温下,羟胺-O-磺酸和酮、醛的反应会产生对应的肟-O-磺酸或其盐。[17]在更高温下,醛肟-O-磺酸会和硫酸发生消除反应,生成腈。[18]

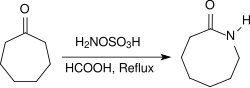
脂肪酮在同样的条件下会产生酮肟,芳香酮则会通过贝克曼重排反应重排成酰胺。环酮和羟胺-O-磺酸在酸性条件(例如浓甲酸中)回流加热几个小时,可以得到内酰胺。[19]
在碱性条件和伯胺存在下,羟胺-O-磺酸可以和醛、酮(例如环己酮)[20]反应生成二氮杂环丙烷,而二氮杂环丙烷很容易被氧化成更稳定的二氮杂环丙烯。
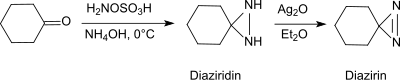
这个反应可用于生产取代的二氮杂环丙烷,并有对映选择性。[21]
1,2-苯并异𫫇唑可以由羟胺-O-磺酸和水杨醛反应而成,[22]而苯并异𫫇唑是抗精神病药利培酮和帕利哌酮以及抗癫痫药唑尼沙胺的母体化合物。

其它反应
[编辑]鲁米诺/氯化亚钴体系发出的光可以被羟胺-O-磺酸显著增强。[23]
参考资料
[编辑]- ^ 1.0 1.1 来源:Sigma-Aldrich Co., product no. 480975 .
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Datenblatt Hydroxylamin-O-sulfonsäure zur Synthese [Hydroxylamin-O-sulfonsäure zur Synthese安全信息单(MSDS)] (PDF). Herstellers Merck (德语).
- ^ 3.0 3.1 Erdik, Ender; Saczewski, Jarosław, Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic Acid, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2013-04-22, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rh058.pub2
- ^ 4.0 4.1 Matsuguma, Harold J.; Audrieth, Ludwig F.; Wehrmeister, Herbert L. Hydroxylamine-O-Sulfonic Acid. Inorganic Syntheses 5. 1957: 122–125. ISBN 9780470132364. doi:10.1002/9780470132364.ch32.
- ^ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils. Sulfur Compounds of Nitrogen. Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. 2001: 675–677. ISBN 978-0-12-352651-9.
- ^ 6.0 6.1 Wallace, Raymond G. Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid – a versatile synthetic reagent. Aldrichimica Acta. 1980, 13 (1): 3–11 [2022-09-08]. (原始内容存档于2019-04-04).
- ^ Rademacher, P. Product Class 7: Hydrazines and Hydrazinium Salts (40.7.1.1.9.2 – Using Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic Acids. Enders, Dieter; Schaumann, E. (编). Compounds with One Saturated Carbon–Heteroatom Bond: Amine N-Oxides, Haloamines, Hydroxylamines and Sulfur Analogues, and Hydrazines. Science of Synthesis: Houben-Weyl Methods of Molecular Transformations 40b. Georg Thieme Verlag. 2014: 1171. ISBN 978-3-13-172181-5.
- ^ US patent 3281209,Wehrmeister, Herbert L. & Harold I. Yalowitz,「Process for the preparation of hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid」,发表于1966-10-25,发行于1966-10-25,指定于Commercial Solvents Corporation (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Baenziger, Norman C.; Belt, Roger F.; Goebel, Carol V. Crystal structure of hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid. Inorg. Chem. 1967, 6 (3): 511–514. doi:10.1021/ic50049a017.
- ^ Erdik, Ender. Hydroxylamine-O-Sulfonic Acid. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. 2001. ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rh058.
- ^ Labarthe, E.; Bougrine, A. J.; Pasquet, Véronique; Delalu, H. A New Strategy for the Preparation of N-Aminopiperidine Using Hydroxylamine-O-Sulfonic Acid: Synthesis, Kinetic Modelling, Phase Equilibria, Extraction and Processes. Advances in Chemical Engineering and Science (Scientific Research Publishing, Inc.). 2013, 03 (02): 157–163. ISSN 2160-0392. doi:10.4236/aces.2013.32019.
- ^ R. Gösl; A. Meuwsen. 1-Aminopyridinium iodide. Org. Synth. 1963, 43: 1. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.043.0001 (德语).
- ^ Campbell, C.D.; Rees, C.W. Reactive intermediates. Part I. Synthesis and oxidation of 1- and 2-aminobenzotriazole. J. Chem. Soc. C. 1969, 1969 (5): 742–747. doi:10.1039/J39690000742.
- ^ T.M. Klapötke; D.G. Piercey; J. Stierstorfer. Amination of energetic anions: high-performing energetic materials. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41 (31): 9451–9459. PMID 22751656. doi:10.1039/C2DT30684K (德语).
- ^ R. Appel; W. Büchner; E. Guth. Zur Kenntnis des Imins, I. Über Phosphinimine und Sulfinimine. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1958, 618 (1): 53–58. doi:10.1002/jlac.19586180107 (德语).
- ^ S.L. Graham; T.H. Scholz. The reaction of sulfinic acid salts with hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid. A useful synthesis of primary sulfonamides. Synthesis. 1986, 1986 (2): 1031–1032. doi:10.1055/s-1986-31862 (德语).
- ^ J. Streith; C. Fizet. Nucleophilic versus electrophilic properties of the nitrogen atom in O-sulfonyl-hydroxylamine derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18 (37): 3297–3300. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)83223-8 (德语).
- ^ C. Fizet; J. Streith. Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid: A convenient reagent for the oxidative conversion of aldehydes into nitriles. Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 15 (36): 3187–3188. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)91857-X (德语).
- ^ G.A. Olah; A.P. Fung. Hexahydro-2-(1H)-azocinone. Org. Synth. 1985, 63: 188. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.063.0188 (德语).
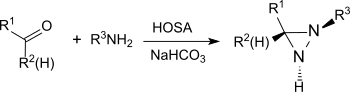
- ^ E. Schmitz; R. Ohme. 3,3-Pentamethylenediaziridine. Org. Synth. 1965, 45: 83. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.045.0083 (德语).
- ^ A.W. Beebe; E.F. Dohmeier; G. Moura-Letts. Diastereoselective synthesis of substituted diaziridines from simple ketones and aldehydes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51 (70): 13511–13514. PMID 26216745. doi:10.1039/C5CC04813C (德语).
- ^ D.S. Kemp; R.B. Woodward. The N-ethylbenzisoxazolium cation—I : Preparation and reactions with nucleophilic species. Tetrahedron. 1965, 21 (11): 3019–3035. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)96921-2 (德语).
- ^ M. Saqib; W. Gao; J. Lai; L. Qi; S. Majeed; M.R.H.S. Gilani; G. Xu. Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid as an efficient coreactant for luminol chemiluminescence for selective and sensitive detection. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51 (30): 6536–6539. PMID 25766485. doi:10.1039/C5CC01090J (德语).
